Child's Silent Battle: The Shocking Truth About ASD and VSD disease.
When the heart pumps, the pressure generated while contracting by the left ventricle is much more than that generated by the right ventricle. Blood will then be pushed through the shunted or VSD from the left to right ventricle. In this procedure, the right ventricle has to do extra work to handle the extra blood volume. This affects the ability of the heart in pumping properly. Under this high pressure, the lungs start getting more blood. This extra pressure leads to permanent damage to the lungs.
Conventional Systems: this requires lesser effort on the patient’s end as far as the maintenance is concerned. A minor surgical procedure is adopted for replacing the power source when it turns out.
Radiofrequency system: They are designed to sustain a longer period of therapy for the highest output levels. Owing to the higher power capabilities, the radiofrequency system is suited for more complex processes with multi-extremity pain. This requires the patient to wear an external power source in order to activate the stimulation.
Rechargeable Systems: This is the newest type of treatment. The patient holds himself responsible for charging the source. This rechargeable system runs longer than its conventional counterpart. A minor surgical procedure might be needed in order to replace the power source.
Patient Selection Criteria
- A patient must not be associated with any kind of malignancy
- A patient must not have any major psychiatric disorder
- A patient must be willing to stop any inappropriate drug prior to the implantation
- A patient must not have any litigation
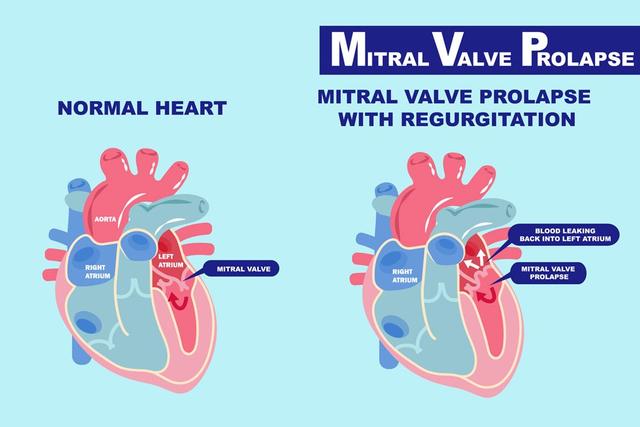
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
Atrial septal defect means a hole in the septum which means a hole in the wall between the atria. This defect causes the blood to flow through a hole from the left to the right atrium. This pressure increases the blood volume in the right atrium which therefore means more blood in the lungs. If this defect is not treated well on time then this can cause serious problems in the future namely weakening of heart muscles, atrial arrhythmias, and pulmonary hypertension.
Treatment of ASD
In some cases, ASD may close on its own without treatment. The rate of spontaneous closure can be as high as 80% in the first 18 months of life but an ASD present till the age of 3 can never close on its own.
Open Heart Surgery: Open heart surgery is not very common these days, however, it is still considered to be a low-risk surgery and effective. Surgeons treat the ASA depending on the size and shape of the hole.
Transcatheter Device Closure: taking into consideration the size and shape of the septum involved, many ASDs can be closed effectively with the help of placing a device while cardiac catheterization. The device is inserted with the help of a catheter and it covers the ASD by attaching to the atrial septum. A catheter is a thin, long tube that is directed into the heart through a large blood vessel in the groin.
Atrial Septal Defect Closure Results:
This is a complication-free procedure in over 99 % of the cases. Though the Amplatzer device has been in use for a short time, its success rate appears to be very high. After the ASD closure in childhood, the heart returns to normal size over a period of 6 months. Post-surgery, there are no problems with physical activities. Regular follow-ups are important and are advisable irrespective of closure mode.
Don't know where to start? Leave us a request, and the Marlin Medical Assistance team will arrange your trip for treatment, where you will improve the quality of life and health.
Get in Touch with Medical Experts
Made in NextJs 13, by Digital Transformation Agency - Ima-appweb.com